Have you hit the Edit Check Wall?
Anyone who participates in endurance sports such as cycling or running will have heard of The Wall. It is the point at which the athlete exhausts their glycogen stores, resulting in a feeling of fatigue, the inability to go on.
As a Data Manager in a Study Builder role the chances are that you have experienced something similar, the point at which the logic for an edit check becomes too complex and you have to fall back on a Custom Function. This is the Edit Check complexity "Wall."
Three levels of Edit Check logic
Essentially Rave has three levels of edit check logic:
- Field Checks (Range, IsRequired, QueryFutureDate etc)
- Configured Checks (Rave Edit Checks)
- Custom Functions
Field Checks can be set up with a few clicks and some data entry for expected high and low ranges. They are extremely fast and easy to set up and require little or no testing since they are features of the validated Rave system.
Configured Checks are written using Rave's Edit Check editor which uses a postfix notation (1 1 + 2 isequalto). Rave Edit Checks are flexible and very functional but every Edit Check that is written has to be specified, written and tested making it an order of magnitude more expensive to create than a Field Check. The learning curve for Configured Checks is quite steep since most of us were taught infix notation in school (1 + 1 == 2).
Lastly we have Custom Functions. These are written in C#, VB.NET or SQL and require some level of true programming expertise. Custom Functions are the fallback, the special tool in the toolbox for the truly complex situations. Besides the difficulty of hiring (and keeping) good programmers in the current technical market, Custom Functions have to be specified, reviewed for coding standards and performance impact as well as tested. Because of the level of skill required we want to write as few Custom Functions as possible.
Costs and learning curves
A graph of the learning curves for the different Edit Check logic types might look like this:
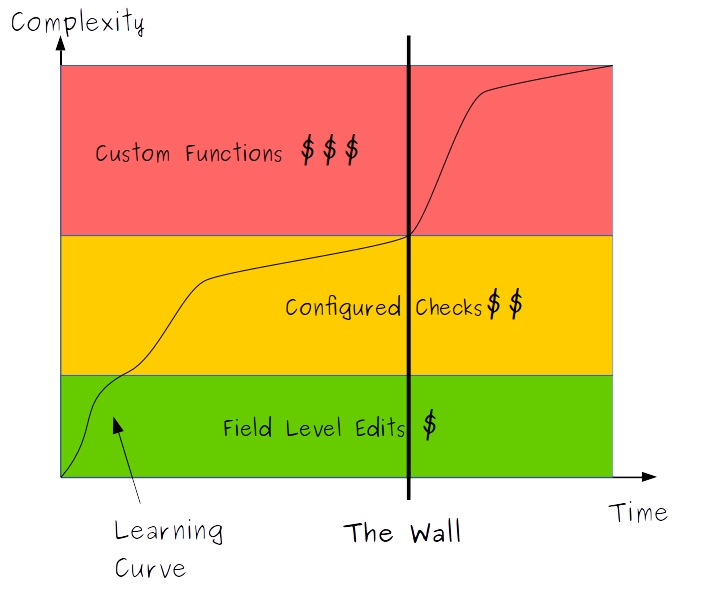
As we can see from the image, Field Checks have a very fast learning curve but they don't get you to a very high level of complexity. Learning Configured checks can be done quite quickly for the basics but mastery takes longer and eventually you reach the Wall where the complexity of a specified check means that you will need to use a Custom Function. We are all familiar with the most simple Custom Function:
1 | |
But doing anything more complicated takes technical training.
Mitigation
The Wall represents the transition from Configured Checks to those requiring Custom Functions. We know that writing Custom Functions is expensive so we want to reduce reliance on them and so move the Wall further away. Some strategies which can be used to do this are:
-
Have standard/parameterized Custom Functions. For instance, instead of writing a custom function to compare specific date and time values, create a parameterized function which can be used for any date and time comparisons. These types of standard functions don't need the same level of validation as a bespoke Custom Function.
-
Analyse the Edit Checks you have written in the past and the queries that they generated. Research on Edit Check complexity in Medidata Rave studies found that the most complex edit checks were the ones least likely to fire. If an Edit Check requires logic so complex that it requires a bespoke Custom Function you may be better off using a manual listing or running the Edit Check as part of other back-end checks.
What we are doing
At TrialGrid we're attacking this challenge with CQL, our Clinical Query Language. CQL is an infix format for Rave Configured Edit Checks.
An Edit Check with CQL (infix) logic like:
1 | |
would be translated into a Rave Edit Check (postfix) logic like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
In fact the translation works both ways, Rave Edit Checks can be instantly translated into CQL and CQL can be translated instantly back into Rave Edit Checks. There is no lock-in here, CQL translates into pure-Rave Edit Checks. Since infix notation is what we all learned in school, CQL is much easier to learn.
But we can do more. CQL includes a set of built-in functions that look like Rave Edit Check functions (IsEqualTo, IsPresent etc) but which automatically generate Custom Functions for you.
For example, We have been asked for an Edit Check that determines if a text field contains non-ASCII characters. Providing a standard Custom Function to do that is easy enough but we go one further and integrate it into CQL.
1 | |
to the user this looks no more complex than the standard Rave IsNotEmpty test:
1 | |
The TrialGrid application takes care of generating the Custom Function. You'll still need some bespoke Custom Functions but fewer and fewer as time goes on and we build more into CQL.
Why wait?
But why wait? TrialGrid allows you to create these function
templates yourself, extending CQL and your Rave Edit Checks with your own private functions that become part of the
CQL language. Want to know if AETERM.IsSigned? or AETERM.HasOpenQuery? Add them to CQL and give your
Custom Function programmers more interesting work to do.
Configuration, not Programming
By using TrialGrid, Edit Checks that would previously have required Custom Functions can now be done by configuration. Our graph looks more like:
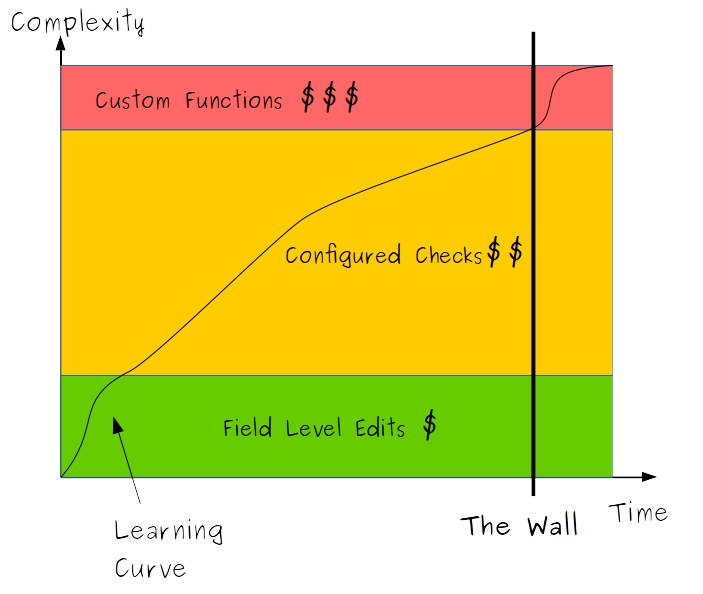
The Wall is moved further away and the learning curve is made much flatter. This is more than just a nice to have, it means more productive Study Build staff and reduced costs. Another step on our journey to reduce the time and effort of Study Build by 50%.
Interested in improving your Rave study build efficiency? Contact us to find out how TrialGrid can help.